Raw and fresh feeding is one of the strongest trends in pet food. But should your dog really have a high meat protein meal every day?
In 2020, researchers - admittedly funded by Hills, so take that into consideration - looked at the impact of varying levels of protein in the diet on the health of beagle dogs. Thirty healthy beagle dogs were divided into groups and fed foods with either low (18.99%), medium (25.34%), or high (45.77%) protein levels for 90 days.
Metabolomics was performed on serum, urine, and faecal samples. The serum chemistry was also measured to assess levels of triglycerides, creatinine, albumin, and cholesterol.
The researchers found that the protein level in the dogs' diet significantly influenced their metabolome (the total number of metabolites present within an organism, cell, or tissue).
Feeding high protein food led to increased microbial proteolytic activity, which is the process by which proteins are broken down into smaller amino acids by the action of enzymes. Furthermore, the study found higher circulating levels of uremic toxins, which are waste products that build up in the blood when the kidneys aren't functioning properly.
The research also highlighted the impact of dietary protein levels on inflammatory markers. The higher protein intake resulted in an increase in these markers, which could potentially result in the deterioration of kidney function over time.
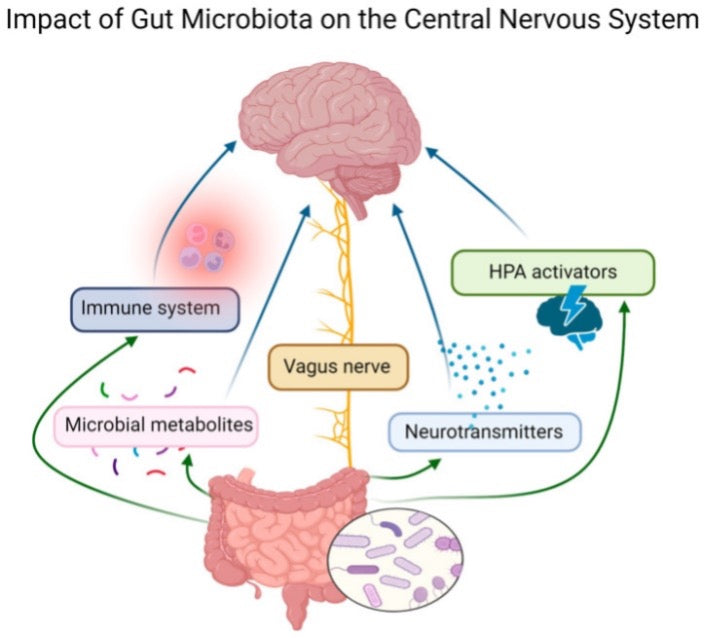
The gut microbiota, the community of microorganisms living in the digestive tracts of dogs, was also significantly affected by the protein content in their diet. The findings indicate that the composition and function of the gut microbiota were altered with varying protein levels.
In summary:
- With high protein food, metabolites associated with inflammation and kidney dysfunction increased in serum, urine and faeces. These include uremic toxins, indole sulfates and p-cresol sulfate.
- Metabolites of one-carbon metabolism like betaine, dimethylglycine and sarcosine decreased with high protein food.
- Faecal pH increased with high protein food indicating increased proteolytic activity of gut microbes.
- Beneficial indoles and short-chain fatty acids decreased while branched-chain fatty acids increased with high protein food.
- Bacteria like Prevotella, Ruminococcus and Faecalibacterium decreased while proteolytic bacteria from families Clostridiaceae and Erysipelotrichaceae increased with high protein food.
The study found that while high protein diets may aid weight loss in obese dogs, long-term consumption of high protein food was associated with metabolites and microbiota changes that could indicate deterioration of kidney function, even though illness was not actually observed in the healthy dogs studied. The results suggest that excess protein intake beyond nutritional requirements may have negative health consequences for dogs.
Why not throw in a Meat-Free Monday to help with this?
References
Ephraim, E.; Cochrane, C.-Y.; Jewell, D.E. Varying Protein Levels Influence Metabolomics and the Gut Microbiome in Healthy Adult Dogs. Toxins 2020, 12, 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12080517